 Treating the Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
Treating the Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
According to the Parkinson’s Foundation, Parkinson’s Disease (PD) affects about one million people in the U.S., and 10 million worldwide.
While there is no cure for the neurodegenerative disorder, a number of medications are used to treat the symptoms of the disease. It is also common for people with PD to take a variety of medications to manage symptoms.
Entacapone Helps Other Drugs Lengthen their Efficacy
Entacapone – first introduced to the market in late 1990’s – is a selective and reversible inhibitor of the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). It is used in combination with levodopa and carbidopa (two Parkinson’s drugs) to lengthen their effect in the brain, reducing Parkinson’s disease signs and symptoms longer than the use of levodopa & carbidopa alone.
Challenges of Manufacturing Entacapone
Entacapone – which went off-patent in 2013 – has subsequently seen a number of novel manufacturing techniques emerge. Many of these production methods suffer from a range of problems which can impact commercial viability at the industrial production scale. Among the challenges of common Entacapone production techniques:

- The technique may yield the wrong isomeric form.
Entacapone exists in two isomeric forms. The ‘E’ form is considered the more pharmaceutically active (and therefore more desirable). - Many techniques use piperdine as a reaction base.
The use of piperdine can lead to the formation of undesirable byproducts. - The technique may use condensation during manufacturing.
With Entacapone, condensation can be time consuming, which negatively impacts yield and leads to product contamination.
- Some techniques may require an extra step of dealkylation.
Dealkylation of 3-alkoxy entacapone can lead to lower yield and purity. - Some techniques use extra acid and solvent purification steps.
The use of additional manufacturing steps is time consuming, and yields tend to be very low. - Techniques may use expensive solvents or chemicals which are not viable at scale.
The use of glycine acetate, for example, is expensive and not viable at commercial manufacturing scale.
Generic Entacapone Delivers Greater Economies of Scale
With Entacapone’s patent expiration, a need arose for generic equivalents to deliver greater economies of scale. (The pricing pressures on generics nearly always make this necessary.) Neuland designed a streamlined process to avoid the use of hazardous and expensive bases and extraneous purification steps.
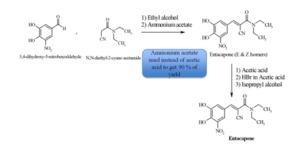
Neuland’s patented method delivers 90% yields (a boost over traditional methods, which yield only 80%) by reacting 3, 4-dihydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde with N, N-diethyl-2-cyano acetamide in the presence of ammonium acetate. Other advantages of the process include:
- Economical: cost effective at industrial scales.
- Eco-friendly: hazardorus & corrosive reagent-free.
- Simplified handling: does not require special temperature condition monitoring.
- Avoids impurities: does not lead to the formation of impurities typically found with piperdine.
 How Does Neuland’s Process Work?
How Does Neuland’s Process Work?
The method developed & patented by Neuland allows for the commercial manufacture of (2E)-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethylprop-2-enamide polymorphic form A. The process includes:
- First, 3,4-dihyroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde with N,N-diethyl-2-cyano acetamide is reacted in the presence of ammonium acetate to form racemic entacapone.
- Racemic entacapone is treated with a catalytic amount of hydrogen bromide dissolved in aliphatic carboxylic acid.
- The (E)-entacapone polymorphic form A is first treated with an alcoholic solvent isolation of the product, followed by further purification with an ester to yield a pure polymorphic form.
- Racemic 2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethylprop-2-enamide (Entacapone) is prepared via condensation of 3,4-dihyroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde with N,N-diethyl-2-cyano acetamide.
- Resolution of racemic Entacapone is performed in the presence of hydrogen bromide dissolved in aliphatic carboxylic acid.
- The crude polymorphic form A of (2E)-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethylprop-2-enamide is treated with an alcoholic solvent.
- It is then purified using an ester such as ethyl acetate.
Entacapone is an excellent example of an off-patent drug where – in order for generic versions to be economically viable – process improvements & efficiencies were necessary. Neuland’s technique checked this box, offering an improved, cost-effective, eco-friendly and easy-to-handle process which yields a substantially purer form of Entacapone at commercial scales.
If you would like to discuss how Neuland can help you overcome your API manufacturing challenges, please contact us.










