Understanding the Drug Substance Manufacturing Process: Key Steps & CDMO Role
The drug substance (active pharmaceutical ingredient, API) is the pure active chemical in a medication. It is the core compound that produces the intended therapeutic effects.
In the drug development process, once a lead compound is identified, chemists must design a manufacturing route to produce this API at scale reliably.
This route must meet stringent regulatory and quality standards (FDA/EMA GMP) throughout development. In essence, the drug substance manufacturing process transforms raw materials into a high-purity API through controlled chemical or biotechnological steps, with quality built in at every stage.
Regulatory bodies (FDA, EMA, ICH) require a detailed description of this process (often as a flow diagram) in filings. All steps are performed under GMP drug substance manufacturing standards to ensure consistency.
Key Steps in the Drug Substance Manufacturing Process
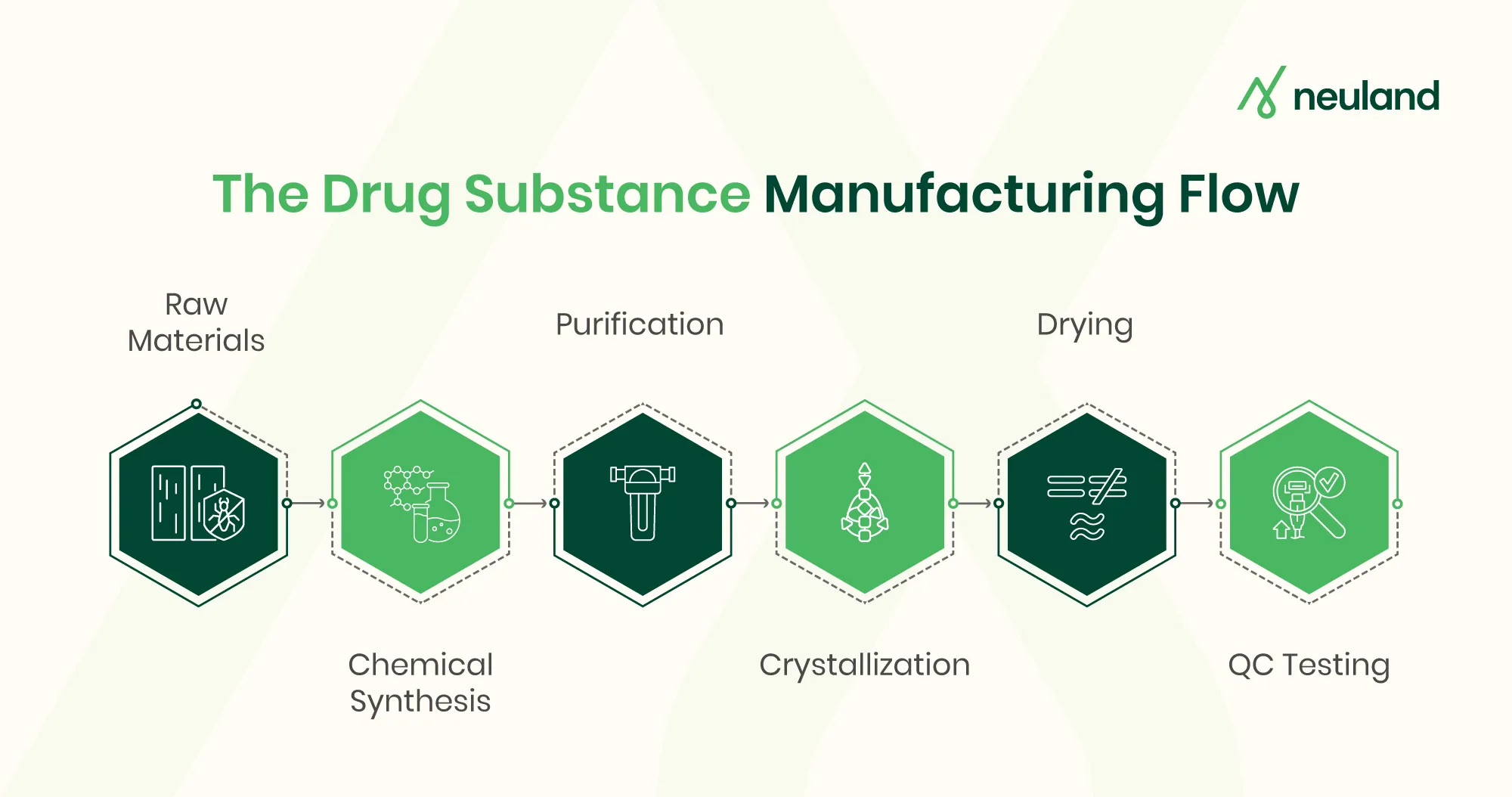
The drug substance manufacturing process generally follows a sequence of steps from initial synthesis to final product testing. Each step must be optimized and controlled under GMP. Typical steps include:
- Raw Material Sourcing – Obtain high-quality starting reagents, solvents, and intermediates with full traceability. Consistent, impurity-free raw materials are a critical foundation for a reliable process.
- Chemical Synthesis/Fermentation – Convert raw materials into the target intermediate or API via chemical reactions (stepwise organic synthesis) or biological fermentation. This “reaction” stage uses designed chemistry to build the desired molecule.
- Purification – Remove unwanted by-products and impurities. Common methods include crystallization, distillation, filtration, and chromatography. Each reaction output is purified to meet strict chemical and physical specifications.
- Isolation & Drying – Separate the purified API from any solvents or mother liquor. For example, the slurry from crystallization is filtered and dried, yielding the solid API. Proper API isolation ensures a stable, dry powder ready for formulation or further processing.
- Particle Engineering (Milling/Micronization) – The dried API is milled or micronized to achieve the target particle size, which can affect solubility and bioavailability. Consistent particle size improves blend uniformity in the final drug product.
- Quality Control Testing – At every stage and especially on the final API, rigorous analytical testing is performed (identity, purity, potency, stability). Only material that passes all specifications proceeds to the next stage or to release. For example, the finished API batch undergoes full QC release testing under GMP to ensure it meets all required quality attributes.
Role of CDMOs in Drug Substance Manufacturing
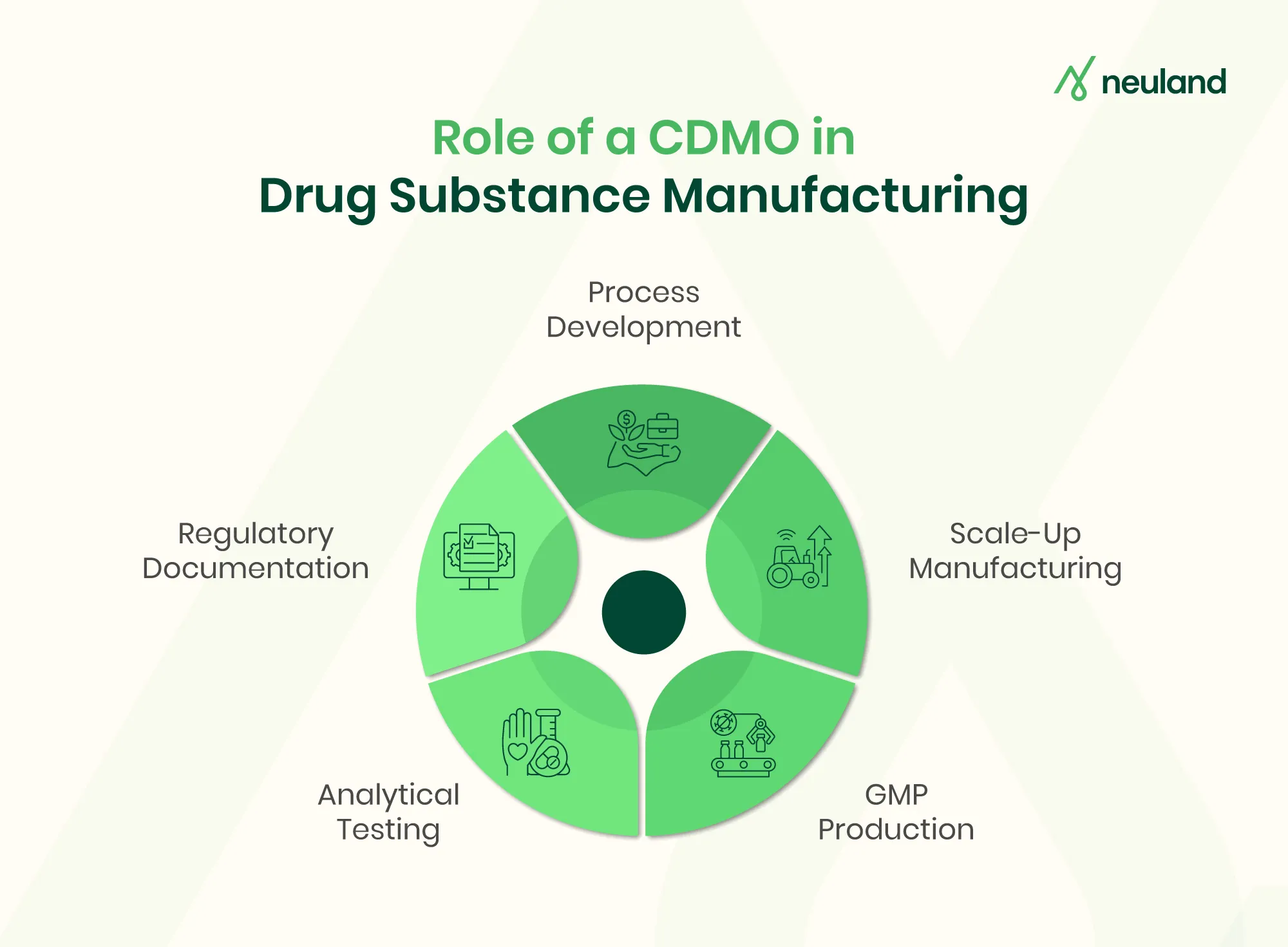
Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) are key partners in the drug substance manufacturing process. By offering pharmaceutical CDMO services, they provide end-to-end support from early development through commercial supply. Working with a CDMO lets sponsors leverage specialized expertise and infrastructure rather than building facilities in-house. Key CDMO contributions include:
- Integrated Development & Manufacturing (Pharmaceutical CDMO Services): CDMOs handle the entire project under one roof – from laboratory process development to pilot and full-scale custom commercial production. This integrated approach accelerates timelines by eliminating hand-offs between multiple vendors.
- Process Development & Optimization in Pharma: CDMO teams focus on process optimization, using quality-by-design and design-of-experiment methods to refine chemistry and purification. Advanced CDMO units routinely optimize reaction conditions and control strategies to maximize yield and robustness
- Scale-Up Manufacturing: CDMOs excel at transitioning a process from gram-scale R&D batches to pilot and commercial volumes. They conduct GMP registration/engineering batches (near commercial scale) to validate performance. Industry sources report that CDMOs typically produce hundreds of grams to multi-kilogram quantities in early phases, scaling to metric tons at the commercial stage. The FDA even allows controlled adjustments during these GMP registration batches, as long as the final process remains representative.
- GMP Drug Substance Manufacturing & Regulatory Compliance: All CDMO operations are performed under strict GMP and ICH guidelines. CDMOs maintain validated facilities and quality systems to meet FDA/EMA expectations. They generate the required documentation for IND/NDA submissions (including CTD sections for drug substance) and run formal validation programs (performance qualification) to demonstrate process control. Clients expect CDMOs to ensure regulatory compliance on time and on budget.
- Modality Expertise: Many CDMOs specialize by drug type. For instance, a small-molecule CDMO brings deep knowledge of organic synthesis, catalysts and crystallization, while a biologics CDMO focuses on fermentation and cell culture. In the small molecule space, some CDMOs (including Neuland) have in-depth expertise in complex chemical routes. Small molecule API manufacturing often involves challenging syntheses and impurity profiles, and specialized CDMOs have the equipment (large glass reactors, continuous units, high-pressure hydrogenation) to handle these tasks reliably.
- Clinical Supply & Flexibility: Early-phase CDMOs can deliver small GMP batches (tens to hundreds of grams) quickly for toxicology and first-in-human studies. Vici Health Sciences notes that Phase I trials may require only 10–100+ grams of API, which R&D-focused CDMOs can produce more cheaply than large commercial plants. CDMOs remain flexible to change batch sizes or multiple dosages as development proceeds.
- Cost & Time Efficiency: By outsourcing, sponsors save on capital investment and share development risk. CDMOs continuously invest in process optimization in pharma (for example, implementing newer catalysts or flow chemistry) to lower costs and timelines. The ability to switch between projects and scales helps avoid delays common in single-product facilities.
Neuland Labs’ Drug Substance Capabilities and Achievements
At Neuland Labs, we provide comprehensive, world-class drug substance manufacturing solutions.
We operate state-of-the-art multi-purpose reactor trains (total 1,174,000 L of capacity) and large-capacity crystallization, distillation and chromatography suites. This extensive infrastructure lets us handle scale-up manufacturing of even the most demanding chemistries.
We have a proven track record of supporting regulatory filings worldwide. To date, we have enabled 25 IND submissions and 4 NDA submissions, providing drug substance for each milestone batch. Our teams have successfully developed and scaled dozens of small-molecule APIs (including HPAPIs and complex intermediates) and peptide APIs under strict GMP/ICH guidelines.
By maintaining global quality standards (FDA, EMA/ICH compliant) across all our sites, we ensure that each drug substance meets international specifications.
At Neuland, we take pride in our pharmaceutical CDMO services: we partner with innovators from molecule development through commercialization, tailoring our drug substance manufacturing process to each client’s needs. Contact us today to learn more.
FAQs
|
|
|
|
|