From Milligrams to Kilograms: Scaling Up Synthetic Peptides
Getting from lab‑scale peptide sequences to multi‑kilogram quantities requires navigating aggregation risks, regulatory standards, and production inefficiencies—challenges that only experienced CDMOs can surmount.
Scaling up synthetic peptides is far more complex than simply increasing batch size; it involves re-engineering processes to maintain purity, yield, and cost-efficiency while meeting stringent GMP requirements.
Partnering with the right CDMO, with the expertise, infrastructure, and track record to manage large-scale peptide production, can determine whether a program has a smooth market entry or stalls.
Key Process Challenges When Scaling Peptides
Scaling peptide production from milligram to kilogram quantities presents technical and operational constraints that extend well beyond simply increasing reactor volume.
Sequence length and aggregation risks
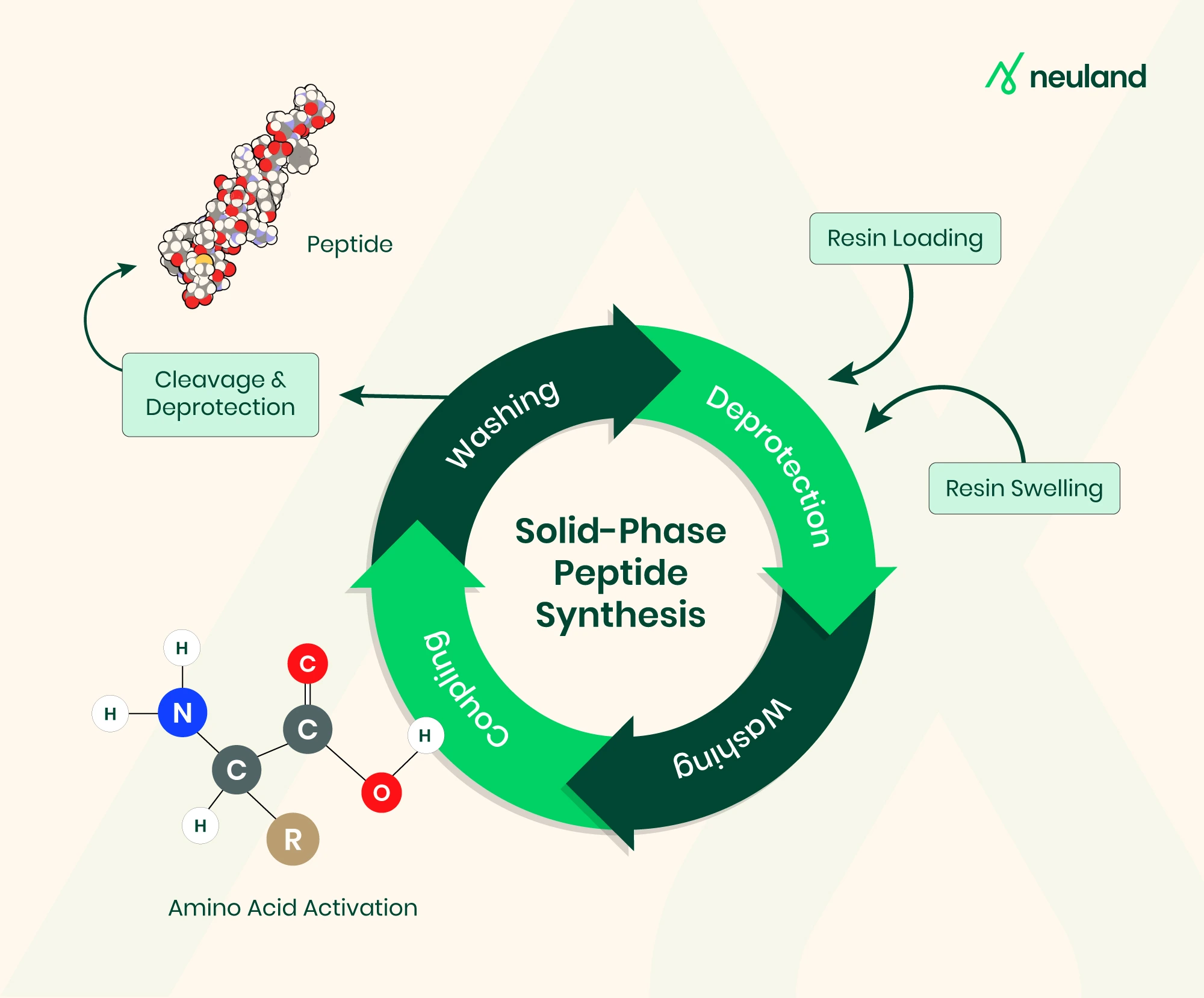
In process development for peptide APIs, sequence length is a critical factor. Solid-phase synthesis yields decline significantly as chain length increases, with sequences beyond 30–40 amino acids approaching the practical limit for SPPS alone.
Extended coupling cycles heighten the risk of aggregation and side reactions, compromising sequence integrity and making downstream purification more complex.
Source: Chemical Wastes in the Peptide Synthesis Process and Ways to Reduce Them - PMC
Material consumption and cost inefficiency
Large-scale SPPS requires substantial quantities of high-value resins, protected amino acids, and solvents.
Because consumption scales nearly linearly with batch size, even minor inefficiencies in coupling or deprotection can translate into significant cost increases.
Strategic integration of solid and liquid phase synthesis at scale—often via fragment condensation—can mitigate some of these costs while maintaining target purity.
Purification and yield consistency
Achieving >95% purity at kilogram scale often necessitates multi-step preparative HPLC and carefully controlled lyophilization.
Longer sequences or hydrophobic segments may require fragment synthesis, enzymatic ligation, or alternative cleavage strategies to improve recovery.
At this scale, any aggregation, degradation, or prolonged hold times during processing can cause notable yield loss, directly impacting supply reliability and cost of goods.

Regulatory & Quality Bottlenecks in GMP Peptide Manufacturing
Scaling peptide synthesis to multi-kilogram levels introduces heightened regulatory scrutiny. GMP production demands strict adherence to facility, process, and documentation requirements to ensure product integrity and regulatory acceptance.
Key considerations include:
- cGMP Compliance at Scale – Large-batch peptide manufacturing requires validated cleanrooms, qualified equipment, traceable batch records, and rigorously trained operators. Stability studies, impurity profiling, and full method validation become mandatory before batch release.
- Regulatory Classification Challenges – Peptides are in a grey area between small molecules and biologics, often governed by ICH small-molecule guidelines, but some classes may require biologic oversight. This ambiguity requires early regulatory alignment and strong justification for impurity thresholds, usually ≤0.1%.
- Analytical Methodology – Higher volumes magnify the impact of minor quality deviations. Advanced analytical methods, including HPLC, LC-MS, and residual solvent analysis, must be validated for large-scale application.
- Skilled Workforce Requirements – Experienced peptide process engineers are limited, and training is essential to avoid errors that can alter stereochemistry or reduce purity. Even small deviations in coupling, cleavage, or purification can result in non-compliance and costly batch failures.
Selecting the Right Peptide CDMO Partner
Choosing the right partner for custom peptide manufacturing is critical to ensuring a smooth transition from early-stage research to commercial-scale supply.
The ability to execute milligram to kilogram peptide production efficiently and compliantly depends on a CDMO’s technical capabilities, infrastructure, and regulatory maturity.
A qualified partner should demonstrate proven experience in both SPPS and LPPS, with the flexibility to apply hybrid fragment strategies when necessary.
Capacity for multi-kilogram batches must be supported by validated large-scale purification systems and lyophilization equipment capable of handling the specific properties of the target peptide.
It is essential to verify that the CDMO operates under ICH, FDA, and EMA-compliant quality management systems, with complete batch documentation, process validation, and audit readiness.
Scaling Up Synthetic Peptides with Neuland Labs
Successfully scaling up synthetic peptides demands precise coordination of process development, purification strategy, and regulatory compliance, particularly for longer or structurally complex sequences.
For R&D leaders and procurement teams, understanding these technical and quality bottlenecks is essential to making informed outsourcing decisions and securing reliable long-term supply.
Neuland Labs exemplifies this expertise, offering SPPS, LPPS, and hybrid synthesis capabilities, large-scale purification infrastructure, and a proven track record in GMP-compliant peptide production. With capacity for multi-kilogram batches and global regulatory alignment, Neuland delivers not only compliance and quality but also the agility and innovation needed to meet evolving peptide manufacturing demands from clinical supply through to commercial launch.
FAQs
|
|
|
|