A Complete Guide to Commercial Manufacturing for Pharma Innovators
As the name suggests, commercial manufacturing is the phase of drug production where an approved drug is manufactured at scale, packaged, and distributed for sale.
The ultimate goal is to optimize proven processes for mass production without compromising quality or safety.
In this blog, we explore what commercial manufacturing involves, how it differs from clinical-scale production, key components and challenges, and why it’s strategically important.
What is Commercial Manufacturing in Pharma?
Commercial drug manufacturing is about producing large volumes of high-quality products for the market. It begins once a drug receives regulatory approval, at which point full-scale production can commence.
This involves converting active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) into finished dosage forms (tablets, injectables, etc.), using well-defined and repeatable processes.
Every step must comply with current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) requirements, and manufacturers break down the process into validated and repeatable steps to ensure consistency.
Clinical vs. Commercial Drug Manufacturing
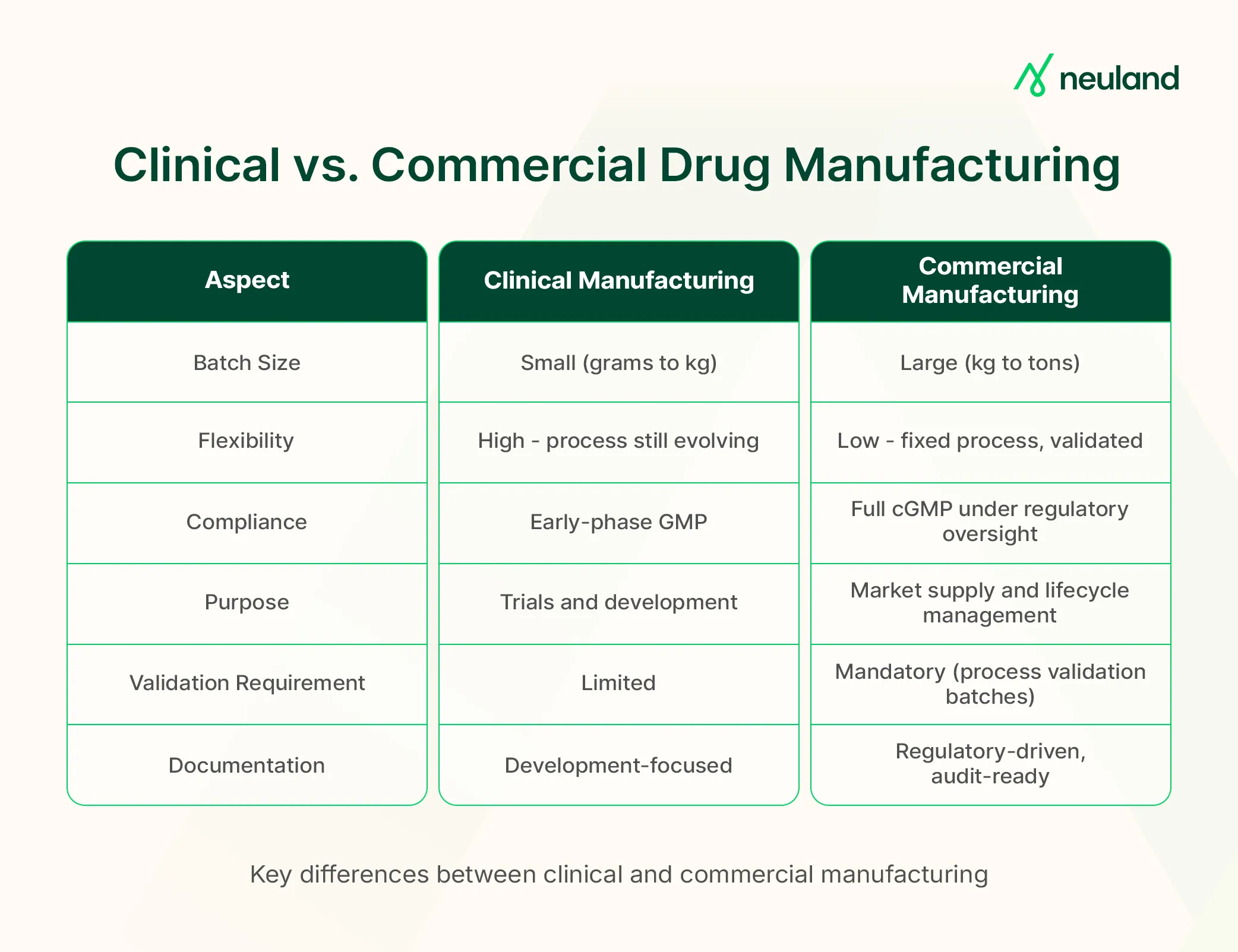
Purpose and Process Stability
Clinical manufacturing typically involves smaller batches made to support ongoing studies. At this stage, the process may still be undergoing refinement, with adjustments to formulation, dosage, or scale.
In contrast, commercial manufacturing requires a finalized and validated process. Once approved, the drug’s formulation and quality attributes are fixed, with a strong emphasis on consistency, efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Oversight and Goals
Clinical batches are used for safety and efficacy testing and can tolerate some variability. Commercial batches, intended for patient use, must follow fully validated processes and meet strict specifications. Commercial production is always under formal cGMP compliance, with deeper regulatory scrutiny.
Documentation and Quality Control
Pilot-scale runs focus on learning and may adapt dynamically. In contrast, commercial drug product manufacturing demands extensive documentation of process parameters, routine quality control testing, and regulatory readiness at all times.
Production Scale
Clinical facilities may produce kilograms of API or a few thousand tablets. Commercial manufacturing plants produce tens to hundreds of tons of API or millions of dosage units, designed for high throughput and long-term supply.
Facility Design
Pilot plants are smaller and built for flexibility. Commercial plants are optimized for sustained, large-scale production with dedicated equipment and streamlined workflows.
Core Components of Commercial Drug Product Manufacturing
Scale-Up and Technology Transfer
Moving from laboratory or pilot-scale to commercial scale requires careful scale-up of the process. Scientists must account for differences in equipment size, heat transfer, mixing, and other factors so that the process yields the same results at larger volumes.
Often, a technology transfer is performed in the process. It involves detailed documentation of process parameters, raw material attributes, and sometimes adapting equipment or process steps to fit the new scale. A successful scale-up maintains product quality and yield even as batch size increases dramatically.
Process Validation
Before full commercial launch, the manufacturing process is put through process validation to prove it can consistently produce products meeting all quality criteria.
Typically, this means running a series of consecutive full-scale validation batches under defined conditions and showing that critical quality attributes are reproducible. Regulatory authorities like the FDA and EMA require validation data as part of the approval.
This step may also include validating analytical methods and other supporting processes.
cGMP Production and Quality Systems
Commercial pharmaceutical manufacturing must strictly follow current Good Manufacturing Practices. cGMP covers everything from facility design and maintenance, to operator training, to rigorous quality control testing and quality assurance oversight.
Every batch is thoroughly tested for potency, purity, uniformity, and contamination, and every process step is meticulously documented and closely monitored.
Quality by Design (QbD) principles often guide late-stage process development, ensuring critical process parameters are identified and controlled. The production environment is carefully controlled to prevent any mix-ups or contamination.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
Commercial manufacturing processes operate within a stringent regulatory framework. Manufacturers must have regulatory filings in place and must produce extensive documentation for each batch to demonstrate compliance.
Global commercial manufacturing also means meeting the expectations of multiple regulatory agencies. Therefore, maintaining data integrity and complete traceability is essential.
Common Challenges in Commercial Manufacturing and How CDMOs Address Them
Transitioning from development to commercial manufacturing is complex. Many pharma companies partner with contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) to overcome challenges like:
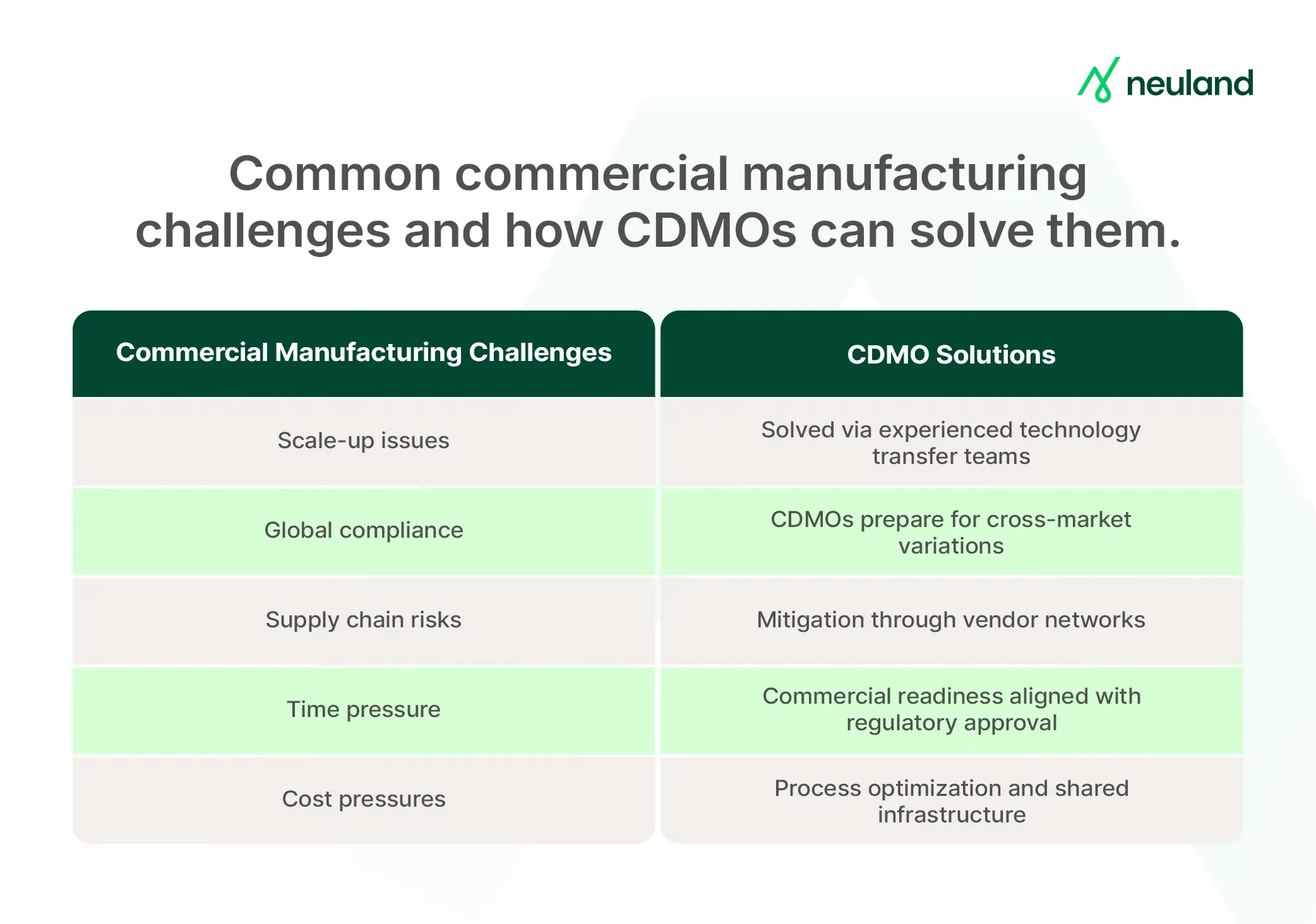
Scaling Up Without Loss of Quality
A process scaled 10x or 100x may behave differently at plant scale. CDMOs conduct thorough process development, use engineering runs, and apply DoE to maintain quality and yield.
Meeting Diverse Regulatory Requirements
Global launches require meeting the expectations of the FDA, EMA, PMDA, etc. CDMOs maintain adaptable systems, generate region-specific documentation, and provide regulatory support to prevent approval delays.
Supply Chain and Raw Material Risks
Shortages, delays, or quality issues can disrupt production. CDMOs mitigate this by having multiple suppliers and maintaining robust sourcing and quality checks.
Timeline Pressures and Capacity
Once approved, patients and revenue depend on supply. CDMOs align validation and inventory build-up with regulatory timelines, often running engineering batches pre-approval to accelerate launch readiness.
Maintaining Cost-Effectiveness
Inefficient small-scale processes don’t always scale. CDMOs optimize yields, recycle solvents, and apply continuous processing. Shared infrastructure spreads overhead and improves unit economics.
Neuland Labs’ Commercial Manufacturing Capabilities
Neuland Labs is a global CDMO with a track record that spans over 4 decades in bringing drugs from lab to market.
The company operates three cGMP-compliant manufacturing facilities in India, with a total reactor capacity of 11,74,000 liters to support commercial manufacturing.
Neuland’s facilities have been audited and approved by major regulators worldwide. This global compliance footprint enables Neuland to produce APIs to the quality standards required for U.S., EU, Japanese, and other markets simultaneously, ensuring uninterrupted supply chains.
Moreover, Neuland continues to invest in expanding its commercial manufacturing infrastructure—boosting peptide reactor volume at Unit-1 from 0.5 KL to 6.37 KL, and adding 52 KL for small molecule manufacturing at Unit-3.
For pharmaceutical companies seeking a reliable partner in commercial manufacturing, Neuland is your one-stop solution.
Contact us today to know more.
FAQs
|
|
|
|