 Data integrity is a key factor for ensuring end products in the pharmaceutical industry meet all quality guidelines. It provides assurance that accuracy and consistency have been maintained throughout the drug life cycle.
Data integrity is a key factor for ensuring end products in the pharmaceutical industry meet all quality guidelines. It provides assurance that accuracy and consistency have been maintained throughout the drug life cycle.
Neuland’s Ashok Gawate, DQA & Regulatory Affairs General Manager, recently wrote a guide to promoting successful data integrity practices.
With attention to data growing, data validation plays a key role in maintaining an organization’s credibility in the pharma industry.
No Small Data Errors
There is no such thing as a small data error: one tiny mistake can call into question the validity of all your data.
A Contract Manufacturer’s Quality systems must have adequate controls to protect the validity of data and procedures for discovering, and more importantly, preventing problems even before they occur. Routine data audits are an effective method of weeding out errors, and a robust training program can decrease the number of innocent mistakes.
Data Integrity Issues
Data integrity problems go far beyond deliberate falsification of data. Untrained employees, disorganized systems and lack of oversight generate more errors and can be more difficult to spot than intentional acts of deception.
While the commitment to data integrity may come from the top, it’s the people in the trenches who are best able to spot and prevent mistakes – if they know where to look.
Data integrity falters when institutions prioritize financial success over product quality. This ultimately trickles down to unrealistic cost controls forcing inadequate investment in staffing, employee training and development, facilities, equipment, systems and controls. Also, leaders who are disinterested in two-way communication or team engagement may indirectly fuel an environment where employees are not empowered to do the right thing.
Preventing Data Integrity Issues
Lack of upper management focus thus results in lack of innovation and continuous improvement, which is integral for data integrity and security. To prevent data integrity issues, drug manufacturers need an atmosphere that fosters the sense that each employee has a responsibility towards data integrity.
A first step is to provide a way for employees to communicate data integrity concerns to managers who have the authority to address problems. Providing a pathway for data integrity concerns to be brought to management’s attention promptly can avoid having these issues discovered during FDA inspections.
A successful data integrity practice in an organization starts from the way training is imparted to the employees. Take a look at your training program and ask these questions:
- Are the right people in the right positions in terms of education, experience and training?
- Do employees have clear roles, responsibilities and accountabilities and do they understand them?
- Do employees have adequate job descriptions?
- Do they know what they’re expected to be doing hourly, daily, weekly, monthly and quarterly?
- Are there enough personnel to execute and provide oversight?
Adjustments in the way employees are recruited, trained and assessed can yield positive results.
Common Sources of Data Problems
Let’s take a look at some common sources of data problems.
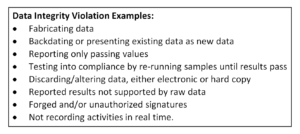 Batch Records Violations are one of the primary sources of data integrity issues. Here are some steps you can take to weed them out:
Batch Records Violations are one of the primary sources of data integrity issues. Here are some steps you can take to weed them out:
- Review records for proper and timely entry of operator signatures and supervisor/management signatures.
- Confirm that dates and times are linear through the batch record execution and appropriate to the process.
- Look for corrections that change the acceptability of the data, such as time changes.
- Look for corrections to bring values into the acceptable range (uncompliant data that suddenly becomes compliant is suspicious).
- Verify suitable document control over batch issuance to make sure there is no ability to recreate, reissue, reprint, duplicate or create an alternate working copy.
- Review raw materials to see if they align when cross referenced to QA release records, material transfer records or other independent sources, and that extra materials weren’t issued.
- Verify that work staff align when cross referenced against personnel work logs, timecards, area entry records or other independent sources.
- Look for delays in progressing to the next step in batch completion and sampling.
- Look for missing data, such as weigh slips, raw materials distribution records, deviations to approved processes, etc. and check batch accountability or yield records for missing product or materials.
Weak Documentation
Weak documentation control opens windows of opportunity for data abuse. To close those windows, avoid:
- Allowing a second or working copy of a controlled document to be printed
- Supplemental records not cross referenced to primary records
- Paper or loose-leaf notebooks, unless their issuance is properly documented and you can verify that they are archived or backed up for audit
- Duplication of documents.
Computer system controls can also impact data integrity. Good general data management controls should provide clear expectations of how data will be generated, reported, reviewed and maintained, including how access to computer systems for generating and modifying data will be limited to authorized personnel, and how data will be protected from tampering.
Pharma contract manufacturing companies should create SOPs that address system change control. These SOPs would govern how data integrity would be maintained during data backup, retention and recovery when changes are made to the computer system.
Electronic Document Control
If you are using electronic systems for data collection, analysis and/or storage, here are a few rules to follow:
- Systems should be validated and validation report should be readily available for review
- Give each authorized user a unique user ID and password to prevent employees from accessing someone else’s system
- Restrict administrator privileges to a select person or people who are authorized to make changes
- Make sure analytical instruments are locked before the analyst walks away
- Limit the use of electronic file folders and establish specific file and folder naming conventions to help identify aberrant data
- Make sure you know who is using the system and what they are doing at all times
- Verify user access permissions are appropriate to the job responsibilities
- Maintain audit trails.
Data Integrity in Laboratory Testing
Data integrity is essential in laboratory testing. You need to make sure that all procedures are clearly spelled out and understood. Check what notebook to use for data recording, which analytical method to use, how to cross reference data in other sources – all these need to be taken into consideration.
Investigations of lab nonconformities can also be problematic. You need to know that those conducting the investigation have really gotten to the heart of the problem, starting with the initial analysis of results and reviewing all investigation documentation and steps taken during the investigation.
Questions you need to ask include:
- What data did the investigation team report?
- What data did they include for final batch release?
- Did they include all of it, including the initial analysis so the quality assurance department has the full picture of what occurred during the investigation?
- If extra or duplicate testing is performed, it should be justified and approved by management or QA before conducting the testing.
In addition to reviewing documentation, observing the lab itself can help you spot data integrity issues. Take a walk through, considering these factors:
- The lab should appear safe, clean and organized
- All equipment and chemicals should be appropriately labeled
- Expired chemicals should not be present
- No personnel unrelated to testing should be present and staff should be recording results in real time.
- Most importantly, loose pages of notes, calculations, etc., should not be lying around or stuffed in drawers. Unsecured records area common source of falsified data and should be investigated immediately.
The Pharma Manufacturing Area
To maintain data integrity in pharmaceutical manufacturing areas, check if:
- Equipment and supplies are present, properly labeled and properly recorded in batch records
- Log books are in place and used regularly
- The area is free of notes, loose leaf memos/papers or other uncontrolled documentation
- Supplies are well within expiration dates and are being properly released by quality control
- Batch records are with personnel while manufacturing steps are taking place and equipment calibrations are current.
Another useful technique is to interview employees regarding their areas of responsibility. Ask where their instructions/SOPs are found and how problems are addressed.
Managing Turnover – in Both Equipment & People – to Ensure Data Integrity
Staff turnover can be an issue for some companies, as it is rare these days for people to stay with the same company for decades. This means the hiring and training of new employees is more frequent, leaving opportunities for inexperience or insufficient training to cause data integrity problems.
Likewise, equipment must be maintained and periodically replaced with newer machinery; both instances offer opportunities for data integrity failures to occur. If implementation of a new piece of equipment isn’t done properly, for instance, that can cause data issues.
Addressing these issues is critical to the process of maintaining data integrity. Utilizing best practices – in conjunction with top-down support – can serve to improve both compliance and operational efficiency.










